galaxies
Galaxies, those vast celestial metropolises, are the cosmic rockstars, orchestrating a grand gathering of stars, gas, dust, and dark matter in a celestial rave powered by gravity. They shape the universe's vibe, influencing star formation, space-time fashion, and the distribution of cosmic glitter.
Now, picture astronomers as cosmic detectives armed with cutting-edge gear, acting as shutterbugs capturing the universe's secrets. Their telescopes, grounded and in space, serve as cosmic cameras, exposing the intricate details of distant galaxies and their celestial architecture.
A Journey Into the Classification of Galaxies
- Spiral Galaxies: The spiral arms of these galaxies, emanating from the central nucleus, are of a distinctive pattern. They commonly represent sites of continuous star-formation activity and dwelling areas for interstellar gas and dust particles.
- Elliptical Galaxies: They have round or oval styles with non-aging looks. They are primarily populated by old-age stars, providing fewer opportunities for galaxies to form stars or for interstellar materials to exist.
- Irregular Galaxies: These galaxies turn the norm on their heads, donning weird forms produced by random gravitational elapses. They feature an enormous variety of forms, which vividly portray their dynamic and unpredictable sides.
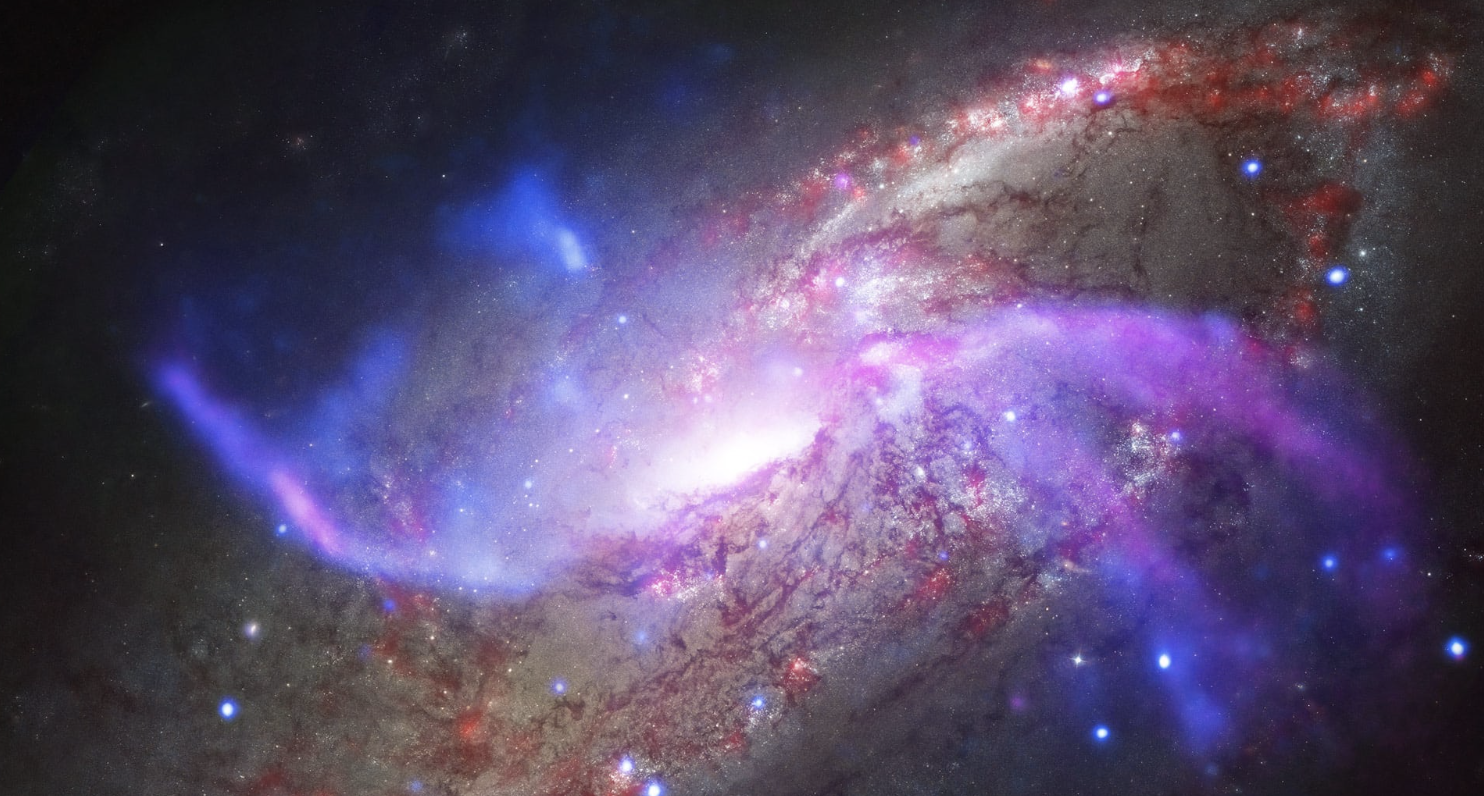

History of Galaxy Formation
The process of galaxy formation involves intricate dynamics between galaxies over cosmic timescales. Galaxies evolve through recurring mergers, close interactions, and feedback loops between stars and interstellar gas – a complex set of phenomena astronomers are still working to map out fully. We can imagine galactic formation unfolding as a progression that began in the early universe after the Big Bang and continues toward an eventual concluding state that is still unknown. Astronomers observe galaxies across wide ranges of distances to reconstruct the detailed sequential steps of how they took shape.
There remain open questions about how galactic constituents – dark matter, gas, dust, stars – assembled in the elaborate structures we observe today. The field can be compared to analyzing a complicated sequence for which the outcome has not yet been revealed.
The investigation into galaxies' formative progression calls for compiling findings across all epochs to tell the developing story, which astronomers continue collecting correctly. Each discovery provides insight into the grand cosmic history.
Cosmic Mysteries
Cosmic mysteries stretch to the enigmatic phenomena, including the unanswered questions pervading the universe. Might this range from dark matter and dark energy to the origins of cosmic inflation and the existence of parallel universes? These secret aspects are the sources of enthusiasm for scientists and philosophers, which inspires researchers and leads to the boundaries of human knowledge expansion. While solving the cosmic riddles is our ultimate goal, we begin our voyage embracing space and the vast depths of time to reveal the hidden imagery of the universe and man's position inside it.
What's the deal with dark matter, the cosmic heavyweight shaping a galaxy's mass? And what about dark energy, the cosmic speedster driving the universe to expand faster? These questions keep astronomers on the edge of their celestial seats.
The combined effects of gas cooling and collapsing, along with dark matter's gravitational scaffolding, facilitate the emergence of early galaxies from widely dispersed gas following the Big Bang. Astronomers continue studying these mechanics of galactic assembly from precursor materials, yielding insights into cosmic evolution.
Dark matter plays an essential role in galactic birth by accelerating the consolidation of gas clouds. As an unseen mass component, dark matter's gravitational influence helps bring together the ordinary atomic matter from which young galaxies arise. So, while gas provides the essential ingredients for star formation, dark matter operates as an architectural framework guiding the construction of galaxies by concentrating hydrogen clouds into dense pockets.
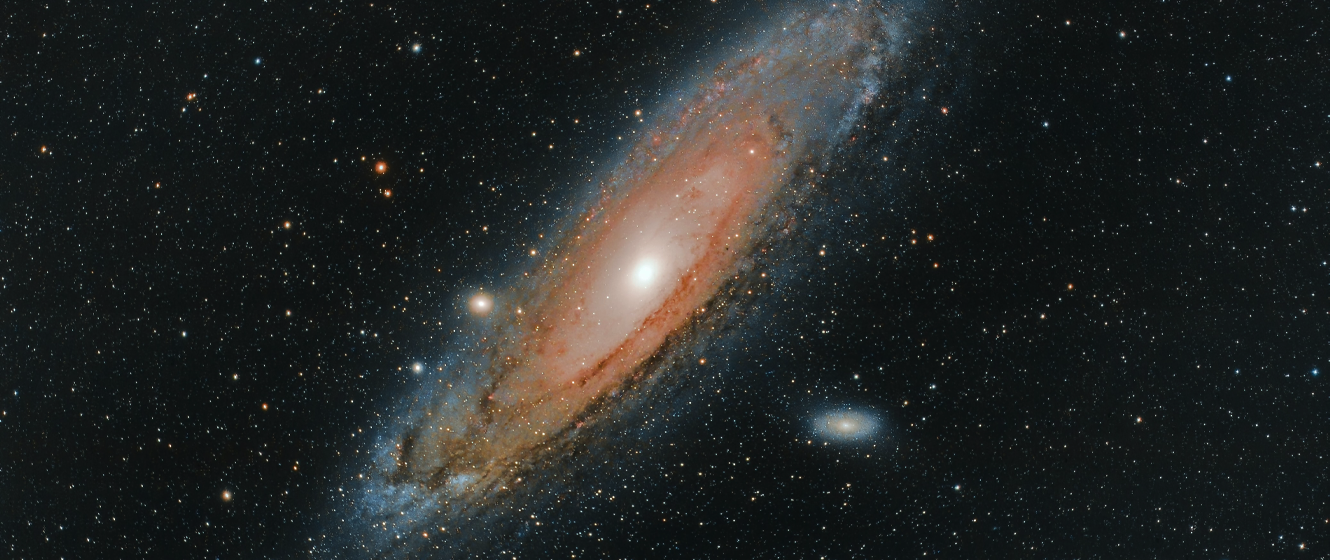

Exploring the Galaxy
Unlocking the mysteries of galaxies involves various observational techniques. Optical observations capture visible light, decoding details about stars, gas, and dust. The cosmic photoshoot, akin to glamorous astrophotography, uses advanced telescope cameras to unveil hidden celestial beauty.
Adaptive optics act like cosmic glasses, overcoming Earth's atmospheric challenges for more precise views of distant galaxies. Exploring galaxies isn't just about stars; it's a journey advancing cosmic knowledge, revealing insights into celestial structures' formation, evolution, and dynamics.
Andromeda Galaxy has been a mesmerizing spectacle to see in the sky at night for a long time. Still today, it's often compared with a cloud, looking like another prime companion of Orion and Lagoon, somewhat distant nebulae. But there is yet another dimension to the story of the Andromeda.
Novas, or exploding stars, have made Andromeda Star a giant story and a mind-blowing sight to enjoy. The once supporting character of our galaxy's story has now become the leading performer, eclipsing the magnificence and mystery of our galaxy.
Galaxies serve as cosmic laboratories, offering valuable data astronomers use to piece together the intricate puzzle of the universe's fate. By studying their distribution, movements, and interactions, scientists can refine cosmological models and make predictions about the long-term destiny of our vast cosmic home.
What should be the very first objective of the beginner’s guide to the galaxy?
This rudimentary guide to the universe is the newest product for those starting in astronomy, designed to be entertaining and valuable as the new astronomy experts while opening a window to the marvelous cosmos outside of our home. It also looks at seasonal factors and exemplifies how visibility differs in different seasons by giving associated examples of prominent galaxies in each season. It mostly deconstructs the mysteries of the galaxies and encourages beginners to observe and enjoy the universe.
The guide explains observing galaxies, including tips on equipment use and choosing suitable locations with minimal light pollution. It also discusses seasonal considerations, highlighting how different seasons affect visibility and offering examples of prominent galaxies for each season. The guide aims to demystify galaxies and inspire curiosity about the universe, empowering beginners to explore the cosmos.
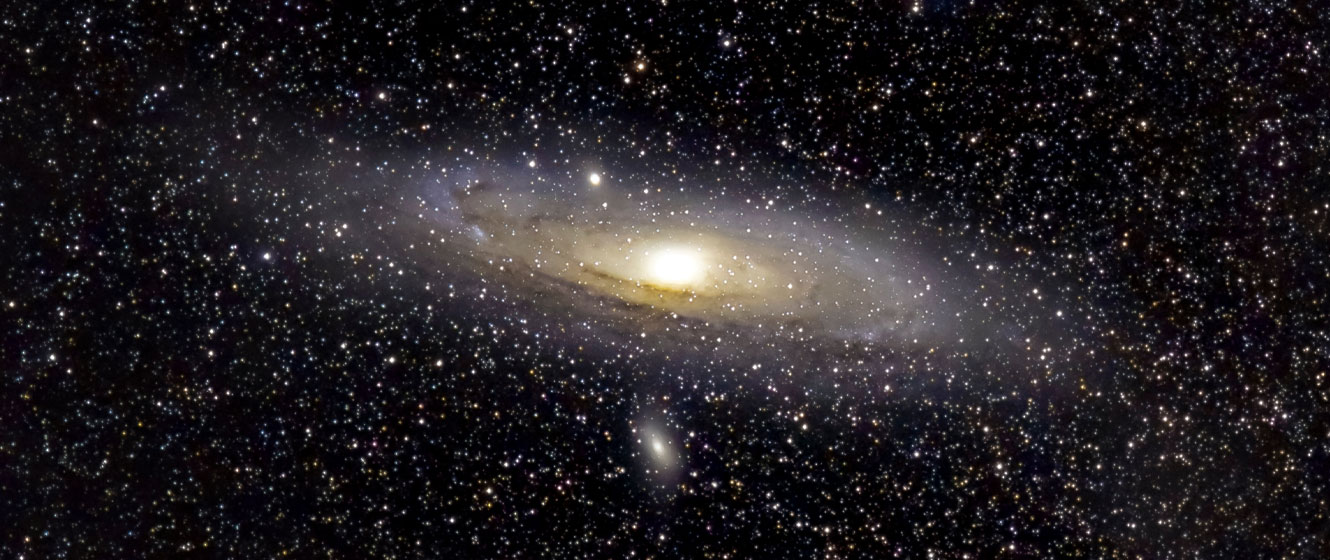

Dwarf galaxies are tiny compared to average-sized galaxies like our Milky Way. Though diminutive, dwarf galaxies far outnumber large ones as satellite companions orbiting significant galaxies.
Theories suggest that it forms through gravitational interactions between central galaxies, resulting in the pulling away of streams of stars. Over time, these stars could coalesce into compact dwarf galaxies. Alternatively, other ideas propose that dwarf galaxies could be remnants stripped from more giant galaxies during close encounters with other massive galactic bodies, leaving only the core behind.
Recent findings favor the stellar stream theory. Dwarf galaxies feature mostly older stars and are dominated by mysterious dark matter, giving clues to their origins. The bizarre shape and composition of the Canis Major dwarf galaxy orbiting the Milky Way reveal it to be an unusually wrecked "galactic tide" slowly being torn apart by the Milky Way's gravity after passing near our galaxy long ago.